As the past three+ years have shown, supply chain disruptions and unexpected demand shifts make forecasting more challenging. However, historical data analytics can help plants transition from reactive to proactive planning and keep planning aligned with operations.
Reporting
Reports provide a visualization of this historized process information and correlate related process variables, compute metrics on that data, and visually graph such data for easier pattern and anomaly detection. These reports are created through third-party software that seamlessly integrates with PLCs, SCADA and historian systems. Advanced reporting solutions can even pull information from remote alarm notification software, allowing further analysis and optimization of condition response times.
Reporting software enables organizations to turn raw process data into actionable information, thereby increasing efficiency and reducing costs. Furthermore, automated reporting solutions streamline regulatory compliance by collecting data from various sources like SCADA, LIMS, manual entry and others. As the data is collected it is summarized as key metrics—flow totals or turbidity threshold analysis. The final output is published into a formatted document accepted by regulatory agencies.
Leveraging aggregated data at the plant level offers economies of scale for managers. With a summation of performance across all machines, larger performance inefficiencies become evident, and managers can develop a deeper understanding of their machine performance, people performance and process performance (machinemetrics.com/production-monitoring).
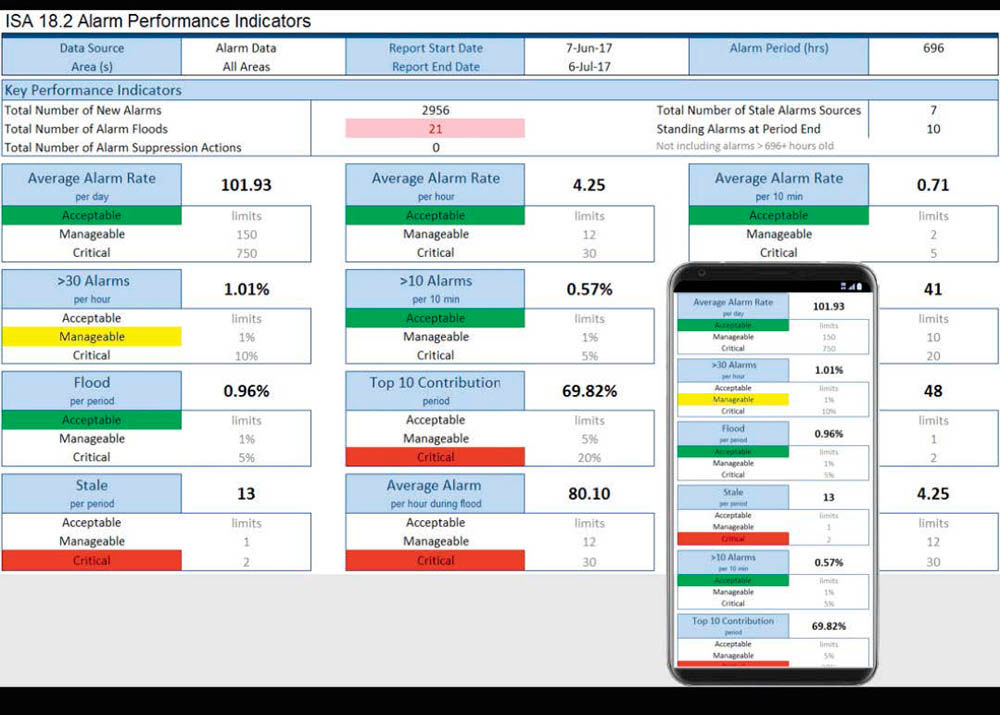
A dashboard showing the Key Performance Indicators (KPI) uses configurable targets to show the health of the alarm system in an “at-a-glance” display.
Alarm Management
A robust alarm management system enhances operational efficiency and enables timely detection of failures. A comprehensive alarm system provides actionable information to the operator and helps in taking corrective action. Research has shown that a well-managed alarm system results in production efficiency, improved product quality and better operator effectiveness.
Since 1991, alarm management standards have been published and currently the ISA-18.2 and IEC 62682 are the most widely accepted. The standards define a seven-step Alarm Management Cycle program from identification to monitoring and assessment.
A cloud-connected alarm management system provides access to real-time alarms even when working remotely to decrease response times and help reduce unplanned downtime. Alarm audits and reporting provide an efficient means to document and track the history of individual alarms, consequences, response time and the action taken to mitigate the alarms. As this rationalization is performed, continued system-level monitoring and assessment reports validate that these efforts are driving real improvement.
An effective alarm management program can help the processes get closer to an optimal operating point resulting in lower production costs, higher quality, greater throughput and eventually safer operations (sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0950423017306320).
Continuous Improvement
The fourth industrial revolution, rapid globalization, technological advancements, changing consumer preferences and evolving government policies are reshaping industries. Trying to meet these challenges with manually intensive processes and outdated technology is difficult. However, by leveraging advanced technology such as real-time alarms and automated processes, operations can increase productivity and efficiency, and reduce costs.
Prioritizing operational excellence not only fosters growth but also positions organizations for continued success.
smartsights.com








