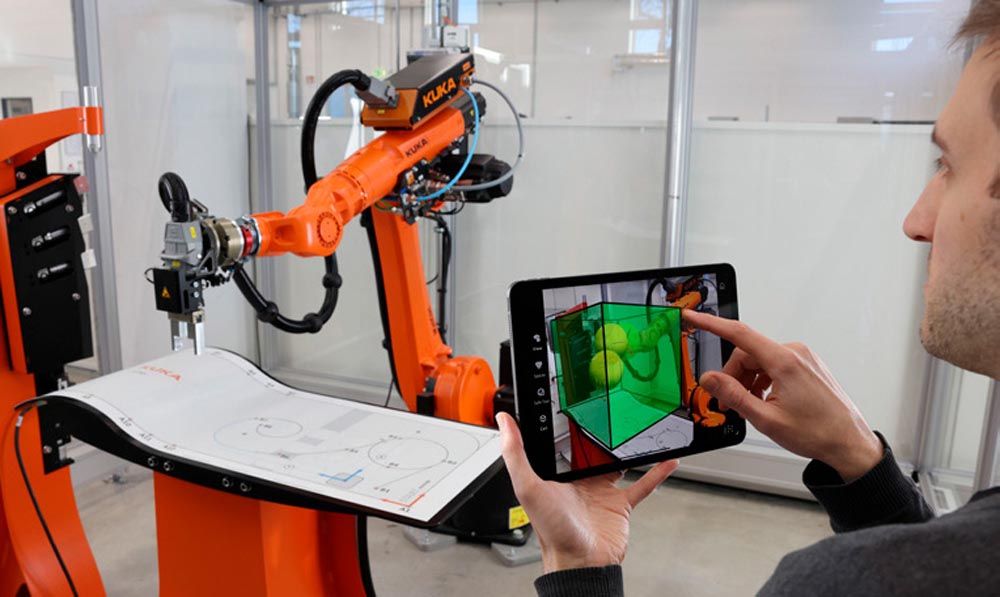
Employing the power of smartphones and Augmented Reality (AR), Kuka has launched its new Kuka.MixedReality software that allows users to visualize the environment of robot cells live on their smartphones to support fast, safe, and intuitive robot startups. The free mobile app displays tools and interference geometries for early detection of potential hazards that can then be eliminated before a robot even starts to work.
AR enables such intuitive robot startup assistance capability, connecting the real and virtual worlds to enrich the environment of robotic cells with clear, uncomplicated digital information. By quickly detecting and correcting errors, facilities accelerate installation and boost safety.
For example, the software will simulate robot motion along with a virtual gripper and detect any potential collisions that arise in the AR environment. These are then resolved at an early stage in the real environment so that neither the robot nor the gripper is damaged.
“Augmented or mixed reality is a future-oriented topic that also offers promising opportunities in robotics,” said Roland Ritter, portfolio manager simulation at Kuka. “Kuka.MixedReality makes robot installation more user friendly and safe. This benefits customers at all levels of experience in the field of automation.”
The Kuka.MixedReality Assistant app graphically displays all relevant variables directly for the robot in real time, including Cartesian or violated monitoring spaces, safety-oriented tools, and tool spheres. Users can also view the corresponding configuration parameters of the spaces or tools.
Kuka.MixedReality is easy to set up and operate. Users simply install the Kuka.MixedReality Assistant on their smartphone or tablet via the Apple App Store or Google Play Store. All relevant information about the robot is transmitted directly to the mobile end device via WLAN through a router or access point—not a Kuka product—and displays visually on the mobile device. AR headsets or additional hardware are not required, and a Kuka.MixedReality safe technology package installs in the robot controller as a data source, along with one of the Kuka.SafeOperation technology packages to use with the safe functions.
Monitoring Robotics in Real-Time
Automotive supplier Booster Precision Components GmbH saves time by efficiently planning maintenance work and transferring diagnostic files. The journey from the decision for Kuka iiQoT to a transparent overview of the entire robot fleet took a mere few days.
The implementation of Kuka iiQoT in a brownfield was quick and easy. On average, we needed about ten minutes per robot. “Now, through networking, we have the assurance that the displayed information is always up to date,” says Tobias Sauer, head of automation at Booster Precision Components. The Kuka iiQoT dashboard bundles all important information transparently and clearly. This way, the robot fleet can be monitored from its location in Schwanewede, Germany—regardless of the robots’ locations worldwide.
“With Kuka iiQoT, Kuka robots become smart robots. Thanks to the clear presentation of the robot fleet, notifications in the event of a fault, as well as status monitoring, our customers gain greater transparency and efficiency,” explains Christian Büchle, platform product manager for Data-Driven Services at Kuka. Through intelligent data collection in the secure Microsoft cloud, customers can minimize machine downtime in their production operations and maximize operating time. For example, the necessary maintenance measures for the robots are transparently displayed in Kuka iiQoT, allowing harmonization for the entire robot fleet. Several Kuka iiQoT functions contribute to quick troubleshooting, such as condition monitoring, which records trends and irregularities. The customer-specific messages support troubleshooting by reporting critical events and fault hotspots for the robot.
Energy Efficiency in Motors and Drives
Sustainability is the name of the game yet many organizations are falling short of original decarbonizing targets. This by no means suggests sustainability is off the table—merely that companies need to reevaluate internal improvements, provide additional electric motor/drive options, and consider adjusting decarbonizing goals in a practical, realistic manner with an appropriate timetable. Industrial automation providers such as Fanuc, ABB, and Yaskawa America can provide a blueprint to help smaller organizations embrace energy efficient components and shop floors.

Linear guides can function reliably in challenging environments—such as Li-ion battery manufacturing—with careful selection, protection, and proper lubrication.
Components for the EV Sector
IKO International recently discussed new EV investments in an automated production infrastructure. There are aspects of EV manufacturing in which specifying an appropriate motion component requires particularly careful consideration. That’s because the heart of the EV—the lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery—poses safety and performance risks that you must keep in mind when selecting motion components. To minimize these risks, it’s important to partner with a supplier that can help you select an appropriate device and offer modification options to meet the distinct requirements of Li-ion battery manufacturing processes.
Although copper is commonly used in Li-ion batteries, its hard-to-detect particles can contaminate the electrode and cause dangerous internal short circuits. Components used in Li-ion battery production should be free of copper-based substances and must not generate dust or dirt. In addition, moisture and humidity hinder Li-ion battery lifetime and performance.
Linear guides can function reliably in challenging environments—such as Li-ion battery manufacturing—with careful selection, protection, and proper lubrication. IKO has extensive expertise and a wide range of protective accessories available to create a custom product that will perform trouble-free.
Changing Markets for Robotics and Automation
In 2023, A3 reported the strongest demand for robots from non-automotive companies came from the metal industry, followed by semiconductor, electronics/photonics, food and consumer goods, life sciences, pharmaceutical and biomedical, plastics and rubber, and others.
While each of these industries showed an overall decline compared to 2022, the last three months of the year saw higher sales in automotive (both OEM and components), metals, semiconductor/electronics/photonics, plastics and rubbers, metals and the All Other Industries category, resulting in an increase of 20 percent over the previous quarter (Q3 2023). The All Other Industries category includes companies in areas such as construction, hospitality and agriculture, typically newer to robotics.
“While robotic sales were down over the year, 2023 ended with both an increase over the previous quarter and a nearly equal number of sales from automotive and non-automotive companies,” said Jeff Burnstein, president of A3. “Both are promising signs that more industries are becoming increasingly comfortable with automation overall. While we expect to see automotive orders rise again, there’s little doubt that orders will increase from all non-automotive industries as they recognize how robots can help them overcome their unique challenges.”
The potential offered by AI-enabled robotics is influencing sectors far beyond manufacturing, according to Segura at ABB Robotics Division. In 2024, these technologies are expected to bring substantial efficiency improvements to more dynamic environments, such as healthcare and life sciences, as well as retail. Another example is the construction industry, where AI-powered robotics can make a material contribution to boosting productivity, enhancing safety and sustainable construction practices while spurring growth.
“The construction industry is a great example of a sector where AI-powered robots will prove transformative, delivering real value by addressing many of the issues facing the industry today, including worker shortages, safety issues and stagnant productivity,” said Segura. “Abilities such as enhanced recognition and decision-making offered by AI, coupled with advances in collaborative robots enable safe deployment alongside workers,” Segura said. “These advances also enable robots to perform key tasks such as bricklaying, modular assembly and 3D printing with greater precision and speed, all while contributing to more sustainable construction by lowering emissions, such as concrete mixing on site, to reducing the need to transport materials across far distances with on-site assembly.”
Automate 2024 takes place May 6–9, 2024 at McCormick Place in Chicago.
automateshow.org