Software and Hardware Advancements for Electrification
Leveraging modularization to address integration and manufacturing challenges related to electrified powertrain systems
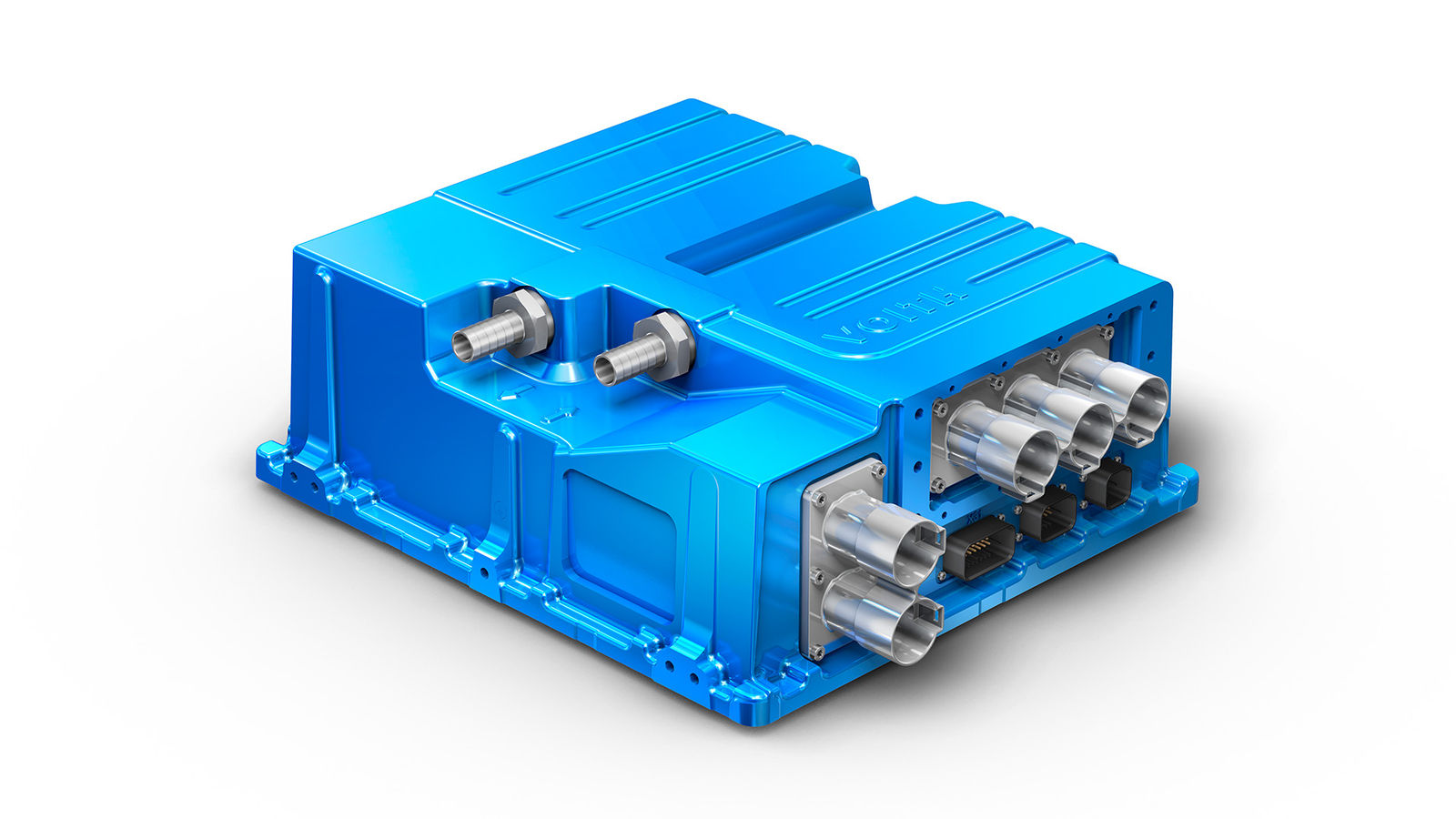
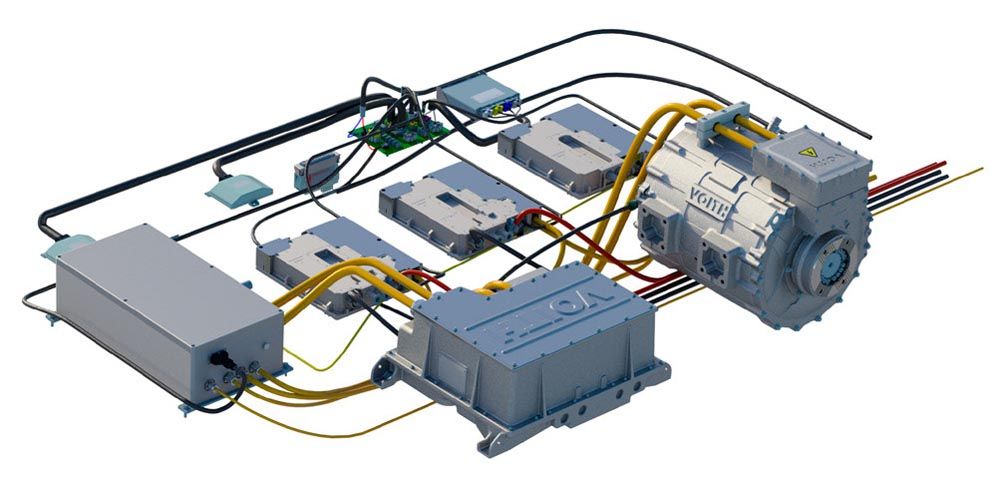
The Next Gen Voith Inverter is modularized with four different power levels, from 150 kW to 390 kW, uses AutoSAR software standards, and complies to ISO 21434—Cyber Security and ISO 26262 (ASIL C)—Functional Safety standards.
The advancement in the technologies for electrified commercial vehicles combined with government incentives for a more sustainable transportation industry, are driving a boost in the demand and deployment of zero emission technologies.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electrified powertrain systems for the transportation sector, manufacturers face a myriad of challenges. From meeting stringent regulatory requirements to satisfying customers’ demands for performance and efficiency, the industry is under constant pressure to innovate.
Additionally, more than any other technology advancement in the commercial vehicle industry in the past, electrification brings the complete symbiose of hardware and software, both equally important elements to the success of the vehicle performance and efficiency. Terms like functional safety, cyber security and others are important parts of the discussions of the development teams at original equipment manufacturers (OEM) and suppliers; researchers; fleets associations; regulatory agencies and government.
One approach that holds significant promise in overcoming these obstacles is modularization of hardware and software. By breaking down complex systems into smaller, interchangeable modules, manufacturers can ensure smooth integration, streamline production processes, enhance flexibility, and improve overall product quality.
Understanding the Software Integration and Hardware Manufacturing Challenges
Before delving into the benefits of modularization, it is crucial to grasp the manufacturing challenges faced by the electrified powertrain sector.