Collaborative Robots on the Rise for the Automotive and Material Handling Industries
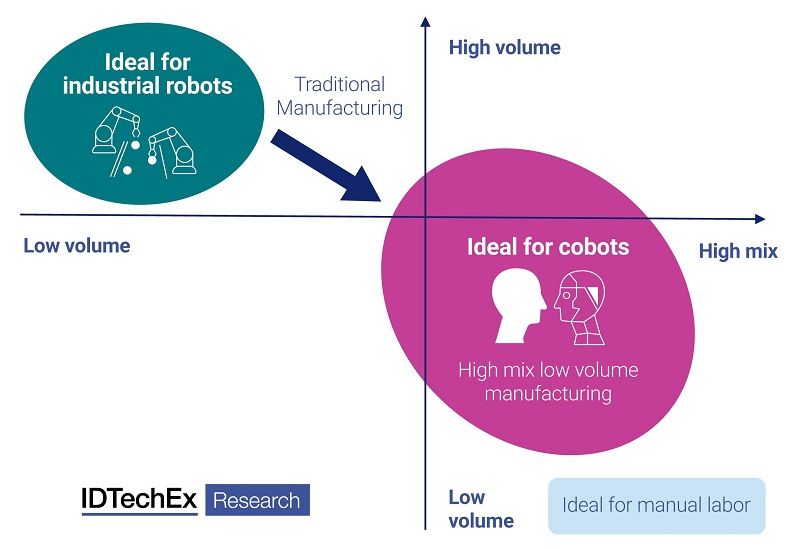
As a pioneer in adopting traditional industrial robots, the automotive manufacturing industry has significantly improved its productivity and efficiency. Although traditional industrial robots have presented significant benefits, one of the fundamental challenges is their high downtime costs. Industrial robots are dangerous and need to be physically separated from human operators. The physical separation means that if a robot malfunctions, human operators must shut all the machines at a production line before entering the robot's working space. This could be problematic as each step of the production is closely linked with the following steps, and stopping the production line will lead to low efficiency and a halt of the following actions or manufacturing. Based on IDTechEx's calculation, an automotive manufacturer's downtime cost per hour could be more than $2 million per factory. Meanwhile, the downtime cost will also lead to a longer delivery time, thereby compromising the company's reputation.
In order to mitigate this issue, many car makers have started to adopt cobots. Cobots are smaller, slower, more flexible, and more lightweight, enabling a safe side-by-side operation with human operators. Most importantly, as there is no physical separation between cobots and human operators, the malfunction of one step in the production line does not affect the regular operation of the rest of the production, minimizing downtime costs.
In addition to the financial benefits, IDTechEx has seen a few emerging regulations and advocacies aiming to bring humans back to factories. Many countries, organizations, and automotive manufacturers have proposed their plans. For instance, Audi proposed 'Automotive Initiative 2025' to achieve an intelligent factory and enhance human-robot interaction (HRI), and the European Commission (EU) proposed 'Industry 5.0', which also emphasizes HRI.
Similar to the trend of industrial robotic arms in the automotive industry, IDTechEx believes that the automotive industry will also be the main target for cobots. At this stage, the adoption of cobots remains relatively low; however, IDTechEx has seen significant growth over the past few years. IDTechEx believes that the market of cobots in the automotive manufacturing industry will have a 130-fold increase in revenue over the upcoming 20 years. IDTechEx believes that with the regulations and financial benefits, there will be a significant number of opportunities (e.g., car assembly, surface polishing, and inspection) for cobots used in the automotive industry. More details about the market size of different tasks of cobots in the automotive industry can be found in IDTechEx's latest report, "Collaborative Robots (Cobots) 2023-2043: Technologies, Players & Markets."
Cobots in Material Handling?
Aside from the automotive industry, material handling, such as packaging, picking and placing, and palletizing, also presents a significant market for collaborative robots.