Mayr ROBA-Guidestop Profiled Rail Brakes Expand Line of Backlash-Free Rails
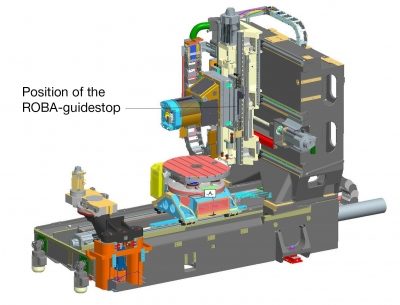
With the ROBA-guidestop-type series, Mayr Power Transmission recently developed a safety brake and backlash-free clamping unit for profiled rail guides, which brakes movements safely and quickly, and which clamps the axes rigidly and backlash-free during the running process. Mayr is now expanding this concept to eight construction sizes, covering nominal holding forces from 5 to 34 kN. The designs are dimensioned for four rail sizes made by linear guide manufacturers. Also new are the compact designs in short constructional design and the integrated switching condition monitoring with contactless proximity switch.
The brake concept clamps rigidly and has a direct effect on the linear guide. The ROBA-guidestop brakes are directly mounted onto the masses to be braked or held. Drive elements between the motor and the moving mass such as spindles, spindle nuts, shaft couplings or gearboxes, have no influence on safety – this differs from concepts featuring a motor brake, in which all drive elements transmit the braking torque up to the carriage, and are often subject to backlash and pole brakes or band brakes.
The ROBA-guidestop safety brakes work according to the fail-safe principle; this means that they are closed in de-energized condition. Pre-tensioned cup springs press the brake shoes onto the “midsection” of the profiled rail and the rail is clamped. The ROBA-guidestop is released hydraulically with a nominal pressure of 70 bar. The brake mechanism is designed for long stroke paths. This means the brake can compensate for manufacturing tolerances on profiled rails without losing its braking force. The ROBA-guidestop safety brakes are designed with two brake circuits working independently of each other. This allows either doubled holding forces or a redundant design.
The backlash-free clamping of the ROBA-guidestop directly onto the profiled rails provides further features: the additional rigidity of the NC axis improves process accuracy and machining performance and can provide further technical advantages, for example in heavy machining. The machining process is less subject to vibrations, which has a positive influence on the surface quality of the part. When the axis is at a standstill, the ROBA-guidestop brake takes over the load. This means that the drive motor can be switched off and removed from the control system during this phase. This eliminates the control movements and relieves the ball screw spindle. The closed brake absorbs axial forces. Downtime intervals and maintenance intervals are extended.





